Tan, Gabriel, Rintala, Diana, Jensen, Mark P., Richards, J. Scott, Holmes, Sally Ann, Parachuri, Rama, Lashgari-Saegh, Shamsi and Price, Larry R. Efficacy of cranial electrotherapy stimulation for neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury: a multi-site randomized controlled trial with a secondary 6-month open-label phase. The Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine. 2011; 34(3):285-296. Download article
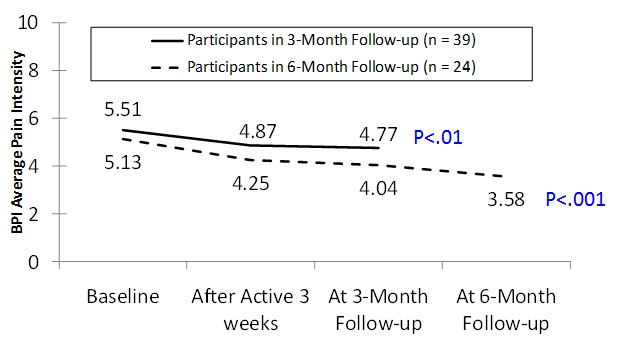
Chronic pain is a significant problem for many individuals following spinal cord injury (SCI). Unfortunately, SCI-related neuropathic pain has proven to be largely refractory to analgesic medications and other available treatments. Alpha-Stim cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) has been effective in managing some types of pain. It involves the application of a small amount of current through the head via ear clip electrodes. The objective of this study was to explore the effectiveness of CES for neuropathic pain in persons with SCI and chronic pain in a multi-site, double-blind, sham-controlled format conducted at 4 Veterans and one civilian hospital. Adults with SCI and chronic neuropathic pain at or
below the level of injury were randomized to receive active or sham CES 1 hour daily for 21 days. A six-month open-label phase was added to assess ‘as-needed’ CES use.
Assessments were made of changes in pre- to post-session pain ratings as well as change in pain intensity, pain interference, pain quality, pain beliefs and coping strategies, general physical and mental health status, depressive symptomatology, perceived stress, and anxiety.