Rintala, Diana H., Tan, Gabriel, Willson, Pamela , Bryant, Mon S., and Lai, Eugene C. H. Feasibility of using cranial electrotherapy stimulation for pain in persons with parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s Disease. 2010. 8 pages. Download Article
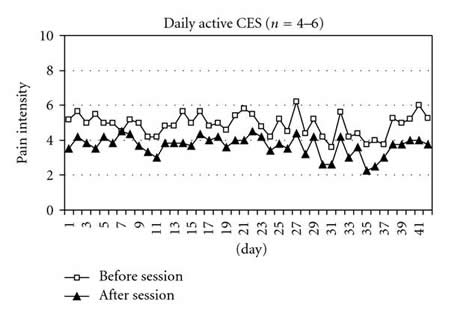
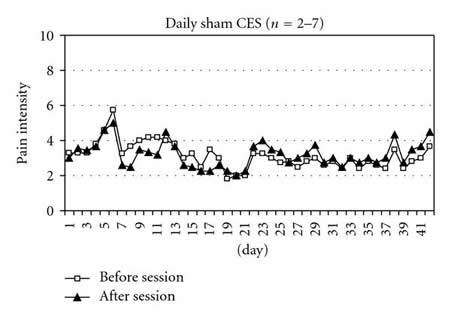
Objectives. To assess the feasibility of treating musculoskeletal pain in the lower back and/or lower extremities in persons with Parkinson’s disease (PD) with cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES). Design. Randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Setting. Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Community. Participants. Nineteen persons with PD and pain in the lower back and/or lower extremities. Thirteen provided daily pain rating data. Intervention. Of the thirteen participants who provided daily pain data, 6 were randomly provided with active CES devices and 7 with sham devices to use at home 40 minutes per day for six weeks. They recorded their pain ratings on a 0-to-10 scale immediately before and after each session. Main Outcome Measure. Average daily change in pain intensity. Results. Persons receiving active CES had, on average, a 1.14-point decrease in pain compared with a 0.23-point decrease for those receiving sham CES (Wilcoxon Z=-2.20, P=.028). Conclusion. Use of CES at home by persons with PD is feasible and may be somewhat helpful in decreasing pain. A larger study is needed to determine the characteristics of persons who may experience meaningful pain reduction with CES. Guidelines for future studies are provided.